Artificial urine is very similar to natural urine in looks, smell, and components. Generally, artificial urine is available in two forms powder and liquid. You can get either form to clear your test. There are several circumstances when synthetic pee is used instead of natural pee. The most common use of synthetic pee is to pass a drug test.
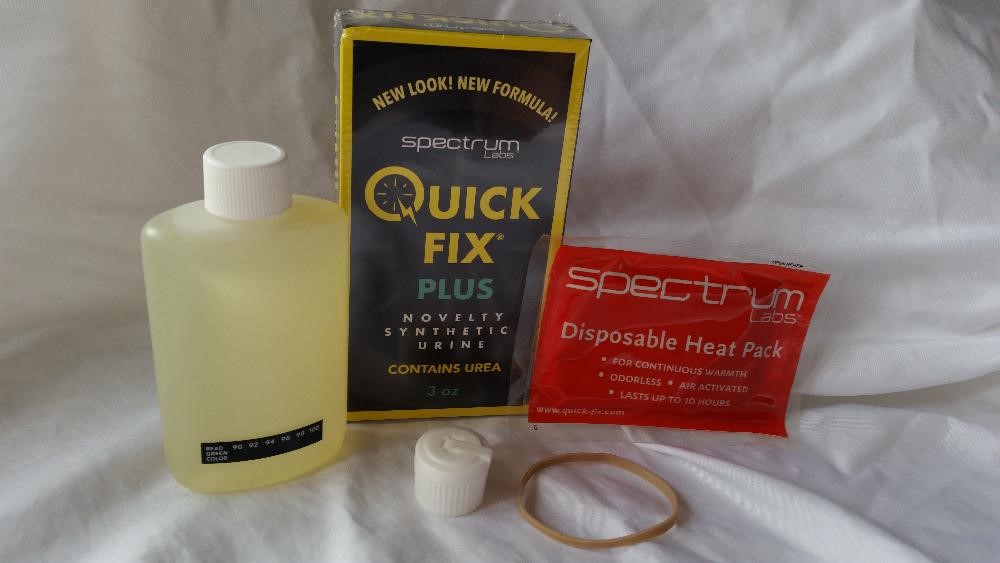
If you are a drug addict, it doesn’t mean that you will fail the drug test. There is still a possibility to change the outcome of a test. If you want to pass the drug test, then it is necessary to buy fake urine. For buying a synthetic pee, it is essential to follow the instructions of the manufacturer.
Here is a guide to know everything about the Best Synthetic Urine brands.
What are the components of synthetic urine?
The formation of artificial urine involves a scientific process, which helps in adding similar features of natural urine to the artificial urine. The synthetic urine also consists of uric acid, urea, sulfates, and ammonia and comes in yellow color, just like natural urine.
Apart from the basic properties, synthetic pee also has the same level of creatinine, temperature, and pH as natural urine. If you are confused about which synthetic urine is best to use, then you can try Quick Fix urine. It is the most reliable artificial urine as it contains the same level of components as natural urine. If you think that your natural urine can get your job at risk, you can use synthetic pee to save your career.
Even if you are not a drug addict but have consumed any drug within a week of drug test, you can’t believe your urine to get a negative result. So, to keep yourself on the safer side, it is recommended to use synthetic pee instead of natural pee. Many companies trade in fake pee, but not all of them are genuine or reliable. Therefore, to avoid any risk, you must buy the artificial pee from the Best Synthetic Urine brands and follow their instructions carefully to produce a positive outcome.
Factors you need to consider while buying the ideal synthetic urine
While going for a drug test, you must use the ideal synthetic users because not all artificial urine is suitable and produce adequate results. So, here are some tips you must consider when choosing the ideal synthetic urine:
Temperature
Your natural urine comes in warm yellow color. The body temperature makes the natural urine warm, and it is generally between 90-100 F. Therefore, it is necessary that the synthetic urine also falls in that range. Ideal synthetic urine comes with testing strips for checking urine’s temperature and also heating pads.
Trustworthy manufacturer
When you search for the synthetic urine market, you will get several manufacturers of it, but not all of them are trustworthy, so you need to examine the reliable manufacturers in the market to not fall victim to any fraud dealers.

Uric acid
It is one of the main components in the urine, so make sure you don’t miss it. So, before buying the ideal synthetic urine, always check the ingredients to ensure uric acid is present in it.
Longevity
An adequate product has a longevity feature, through which you can store it for some time. The drug test doesn’t come with an alarm to alert, so having non-expired urine can serve you the best.
Final words
While buying artificial urine, it is advisable to buy it from Best Synthetic Urine brands. The best brands serve you quality product and provide your multiple benefits